- Home
- About Us
-
Products
.png)
-
Application
.png)
-
Blog
.png)
- Contact us

Optimizing Flame Retardant Performance in PVC Cable Compounds
In the production of PVC cable compounds, balancing superior flame retardancy with physical, mechanical, and electrical integrity is essential. Flame retardancy is primarily measured by the Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI)—the minimum oxygen concentration required to support combustion. For high-safety applications, a material is generally considered high-performing when the LOI exceeds 30%.
1. The Role of Plasticizers
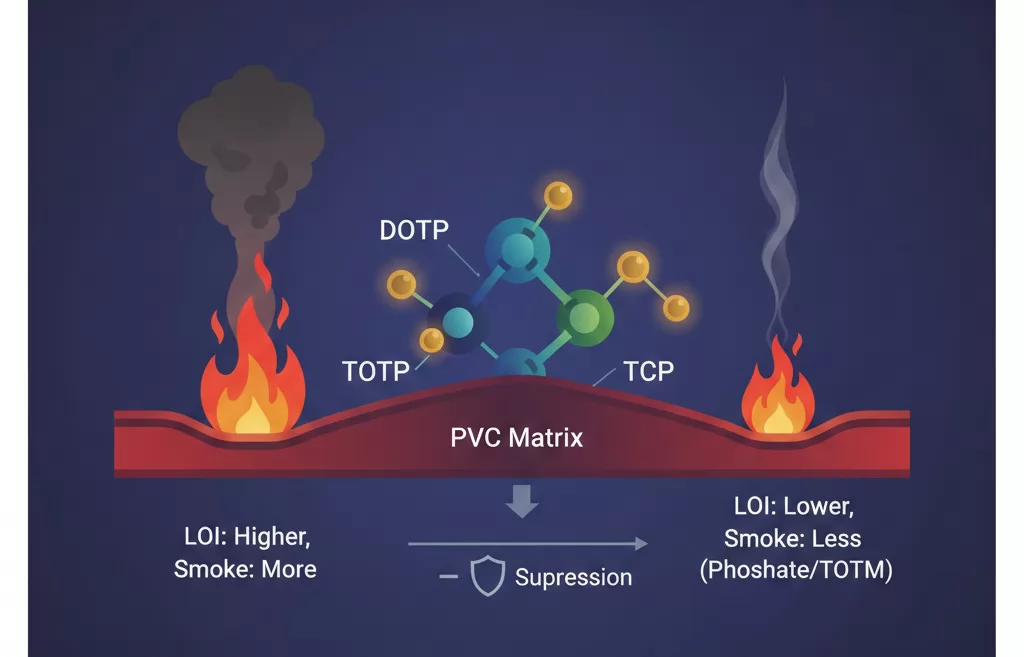
Plasticizers such as Dioctyl Terephthalate (DOTP), Trioctyl Trimellitate (TOTM), and Tricresyl Phosphate (TCP) significantly impact smoke emission and flame resistance:
- Oxygen Index Impact: Research shows that as the proportion of plasticizer increases, the LOI typically decreases across most plasticizer types.
- Smoke Suppression: While most plasticizers increase smoke density, phosphate-containing plasticizers and TOTM provide a synergistic benefit by enhancing smoke suppression in the PVC matrix.
2. Synergistic Effects of Flame Retardants
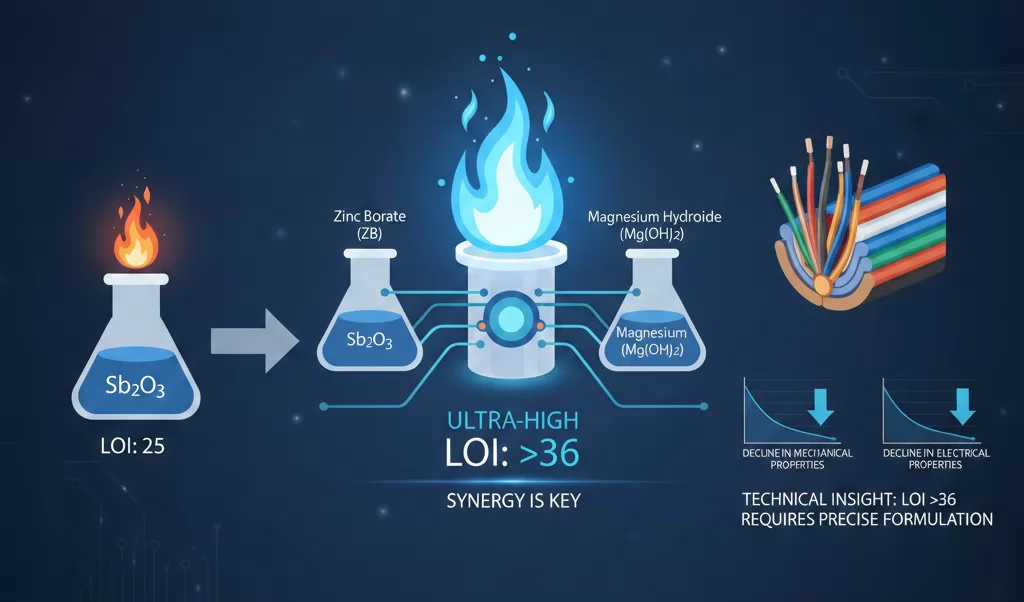
The addition of inorganic flame retardants is the most effective way to boost the LOI. While Antimony Trioxide (Sb2O3) is a standard additive, it has limitations when used alone.
- Synergy is Key: To achieve ultra-high LOI, a composite system is required. For example, combining Sb2O3 with Zinc Borate (ZB) and Magnesium Hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) yields a significantly higher flame retardant effect than Sb2O3 alone.
Partner with KMT Industrial (HK) Ltd
Founded in 2008, KMT Industrial is a leading specialist in the research, production, and sale of advanced flame retardant solutions. We provide the high-purity additives mentioned in this study to help you achieve the perfect balance of safety and performance.
- Hexagonal Magnesium Hydroxide
- Precipitated Magnesium Hydroxide
- Aluminum Hydroxide (ATH)
- Hydromagnesite & Brucite Powder
- R&D Center & 2 Production Plants
- ISO 9001, 14001, 45001 Certified
- Full EU REACH & RoHS Compliance
- D&B Registered (Code: 554405380)
Your Name*
Your Email*
-
2026-Jan-22AM3V: The Next-Generation Flame Retardant Replacing ATO in PVC CompoundsDiscover AM3V, KMT Industrial’s innovative flame retardant replacing ATO in PVC compounds. Achieve high LOI (≥30), low smoke density, and 1/15th the cost.
-
2026-Jan-19How Magnesium Hydroxide Affects Polymer Rheology and ProcessingDiscover how magnesium hydroxide (MDH) affects polymer rheology and processing. Learn expert solutions for optimizing extrusion, injection molding, and compounding of HFFR flame retardant compounds. Technical guide for polymer engineers and manufacturers.
-
2026-Jan-13How to Choose the Best Magnesium Hydroxide Flame Retardant SupplierSelecting the right MDH supplier is critical for HFFR performance. This guide covers technical grades, surface coatings, and global compliance. Learn more with KMT Industrial.

-

 +86-931-7653361
+86-931-7653361 Room 1212, 1213, Jinhe Building, No. 1264 Beibinhe West Road, Anning District, Lanzhou City, Gansu Province, China.
Room 1212, 1213, Jinhe Building, No. 1264 Beibinhe West Road, Anning District, Lanzhou City, Gansu Province, China. -
Quick Links
-
Products